Article on EDGE COMPUTING
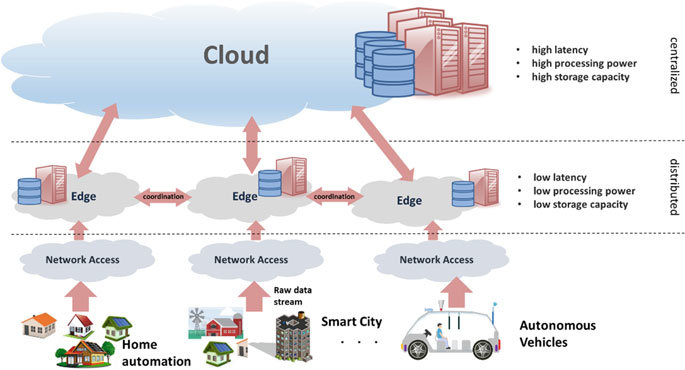
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing structure that enables the data to be analyzed,processed and transmitted to the edge of a network i.e., near the place where data is generated/created (the device itself) or stored (Local computers or Servers) to reduce response time and reduce the load on the cloud server. The edge device on the network could be anything like phones, laptops, smart wearable, industrial robots and sensors that access the rest of the network.
Gartner predicts by 2025, 75% of data will be processed at Edge Network and the rest 25% at cloud or traditional data centers.
How Cloud Computing is different from Edge Computing?
The basic difference between Cloud computing and Edge computing is where the data processing takes place.
Edge computing enables data generated by IoT devices to be analyzed and processed closer to the place where it is produced or consumed in real-time. It can be processed by the device itself or by a local computer or server (also called Mini Data Centers) instead of directly transmitting it across long routes to clouds or centralized data centers.
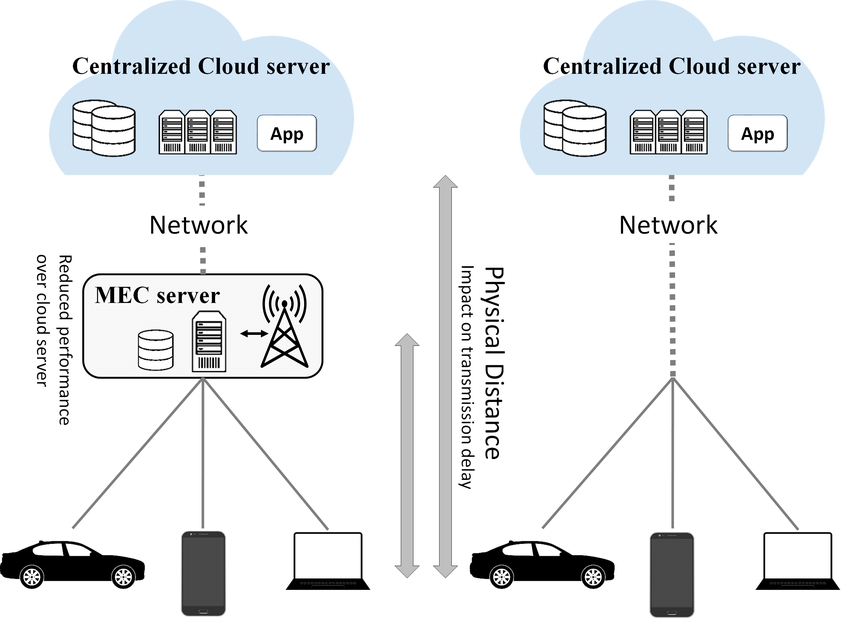
In recent years, we have witnessed exponential growth in the usage of IoT devices that connect to the internet for either receiving information from the cloud or transmitting data back to the cloud. An enormous amount of data generated by these IoT devices during their operations need to be processed. Sending sheer volumes of data from IoT devices for processing to data centers and clouds requires larger and more expensive connections.It overloads available network capacity and in addition to its, the physical distance between the user and the cloud increases transmission latency results in a slow speed of response time and stressing out the user.
This is the reason, need for edge computing arises. If a large volume of data is generated by IoT devices is processed near the data source itself rather than sending it to the cloud or centralized data center, resulting in better internet bandwidth and reduces latency issues and improving data processing capacity and speed. It also eliminates the cost of processing and maintaining huge data in the cloud. Edge computing also reduces network security risk as there is no communication with any public cloud.
Storage Capacity of centralized data centers or cloud offers a much greater density of computing, storage and networking resources whereas in edge computing are smaller distributed data centers that provide a resource-dense midpoint between the edge devices and the centralized cloud with low round trip latencies of 5-10ms.
Advantages of Edge Computing
Real-Time Response Data computation is carried out in place closer to where data is generated; responding to data in real-time can be achieved which is most important in applications like self-driving cars, preventive measures in the manufacturing industry that is advancing towards Industry 4.0 revolution.
High processing speed and low latency Data doesn’t have to travel through the network to cloud or centralized data centers for processing and receiving back processed data to the edge.
Reduced Internet bandwidth usage and cost associated with it Large volume of data can be processed near the source itself, reducing internet bandwidth and cost for storage and computation.
Security As most of the workload is offloaded on edge networks sometimes don’t require networks connection, ensuring full security.
More Reliable Most Mini/Micro Data centers don’t require an internet connection makes them more reliable, robust and secured as compared to the cloud.
Disadvantages of Edge Computing
Security Risks Edge devices and nodes are more vulnerable because they have limited firewall and encryption protections, thus hackers can easily gain access to the network and can steal, alter or destroy sensitive data stored at edge devices. In edge architectures, edge devices like smart wearables, laptops, mobiles are likely to be stolen, lost, broken.
Power Outage Power outages at the edge-centric premises can bring core business operations to stop functioning altogether. Power failure even for one second due to power surges or spikes can put IT equipment at risk (servers, routers), leading to loss of data. Though generators or UPS systems can keep the workloads powered, continuous requests from nodes prevent edge devices from entering power-saving mode causing outages due to battery drainage.
The investment cost for setting up Mini/Microdata centers If an organization has several IoT devices which produces a large volume of data and need lower latency then the organization has to spend on edge infrastructure nearby the factory floor, warehouses, retail shops where the data is produced or consumed. IoT devices with the edge computation require additional hardware and resources for them to function and the investment cost for setting up robust and reliable on-premise server/s is higher.
Maintenance Edge computing is a distributed network. For Example: In the manufacturing unit, a large volume of data is generated by PLC’s, Robots in the machine and IT system are sent to the respective cloud for analyzing and processing. Collecting data produced by several computing nodes to one place becomes challenging and this requires a higher maintenance cost.
Large Storage Space Edge computing with IoT devices requires considerably more storage space.
Incomplete data In edge computing, some part of the workload is offloaded to the edge devices or servers for analyzing and processing the rest of the data are discarded. The organization must ensure which valuable information they want to retain which they are willing to lose before using edge computing.
Does this mean, cloud computing is obsolete?
Edge computing is not a new concept; if we look back into history it was introduced by Akamai who introduced Content Delivery Network (CDN) to overcome web traffic congestion problems. CDN distributes the static content of the website like pictures and videos and keep them in the proxy servers close to the user physical location.
Even with the introduction of edge computing there will still be a need to connect them to cloud or centralized data centers, whether they are on-premises or in a cloud. Cloud computing will still play a big and dominant role in the world of digital transformation. We will try to understand with different scenarios.
Scenario 1: Smart Wearable can monitor health vitals like heart rate, pulse rate, body temperature, glucose level etc. A lot of data is generated by smart wearable sensors throughout the day and stores in a cloud that is not even required. But if the sensor detects some unusual changes in health vitals then relevant data must be sent to the cloud and after identifying the problem, it will send a notification to the emergency number and concerned authorities, so that person in distress can be saved. This scenario is the perfect blend of edge computing, leveraging 5G wireless technology with AI which will help the medical team to work efficiently in the golden hour.
Scenario 2: In the manufacturing unit, machinery used in production operation is equipped with sensors like temperature, motion etc. which monitors the general condition of the machine. To ensure the proper functioning of the machine data from these sensors must be analyzed in real-time to anticipate malfunctions. Data from these sensors is sent continuously to the edge server which is stored and analyzed in real-time. In case of any malfunction or identifying which component is about to fail, an application running on an edge server will trigger an alert to the technical team so that it can be replaced within time, hence reducing downtime. Predictive maintenance with edge computing not only improves operational use but also reduces maintenance costs for repair, lowers spare part inventory.
Scenario 3: AI makes decisions based on data received from multiple sensors in self-driving vehicles such as cameras, RADAR’s and LIDAR’s which give insights into road conditions, pedestrian locations, light levels, things around the vehicle, weather conditions. All these sensors produce a huge volume of data and it must be processed at the edge itself and reacting to any road incidents in real-time to improve safety, reduce accidents. A delay millisecond would be fatal if cloud computing were used.
We can say Edge computing is a decentralized extension of cloud computing.
From the above examples, we can conclude that both Edge and Cloud computing are required.
Real-Life use cases of Edge Technology
- Autonomous vehicles
- Remote monitoring of assets in the gas and oil industry
- Smart grid
- Predictive maintenance
- In-hospital patient monitoring
- Virtualized radio networks and 5G (vRAN)
- Cloud gaming
- Content delivery
- Traffic management
- Smart homes
- Streaming services
Join Famark Community!
Famark community is a social platform for creative and innovative professionals from different domains.
Join Community